Cryptocurrency offers the potential for massive returns on investment. While there have certainly been a few “Bitcoin billionaires,” there have also been legions of others who have done well for themselves even if they didn’t hit the 10-figure mark.
If you’re going to succeed at crypto, you’re going to want a non-custodial wallet. The granddaddy of those is the core wallet. While any wallet keeps track of all the coins and tokens you have on a particular blockchain, a core wallet includes the whole blockchain.
Yes, the whole blockchain.
Core wallets are the real deal. In fact, the first-ever crypto wallet was a core wallet. This is the Bitcoin core wallet.
It’s also known as the Satoshi client. It was created by Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of bitcoin, and released alongside the Bitcoin blockchain in 2009.
Since then, more cryptocurrencies have been created and released. And with them, have come more core wallets. These include core wallets for Bitcoin Cash, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and Dash.
What is a Core Wallet?
A core wallet is a software program that contains a copy of its blockchain. Like any other wallet, it can be used to store cryptocurrencies. In this way, it’s similar to a Metamask or Trust Wallet. You can use it to send and receive digital currencies and manage your crypto balance, but this is as far as the similarities go.
Unlike your regular crypto wallet, this type of wallet stores the blockchain in its entirety. For instance, Bitcoin Core contains the full ledger of all the bitcoin transactions ever done. Your Metamask wallet, on the other hand, will only keep a record of your transaction history.
Core wallets are also more technical than your typical hardware or software wallet. Some even let users program on them. This allows the user to add their own features like a custom user interface, integration with another website or application, transaction trackers, etc.
How Do Core Wallets Work?
Like other wallets, core wallets have private keys and public keys. Private keys give the holder full access and control over the funds in a wallet. Public keys, on the other hand, are a wallet’s address on the blockchain. Unlike other types of wallets, though, core wallets don’t have seed phrases. They only have optional passwords/passphrases.
The information for your Bitcoin Core wallet is stored in the wallet.dat file, which can be password-protected. If you do so, as long as you remember the password, you can change it through the Bitcoin Core client. If you forget it, go through all the passwords that it might be. Write down incorrect choices as you go to shorten this process as much as possible.
Being non-custodial, these wallets generate your private keys for you and store them on your device. This gives you full control over them and thus, unrestricted access to your cryptocurrencies. In contrast, wallets that don’t give you your private keys are said to be custodial.
When it comes to public keys, you can generate new ones for each transaction. You’ll still be able to access your funds since the core wallet stores a private key for all your addresses. This is a security feature aimed at increasing privacy.
Note that using a core wallet requires you to download the entire blockchain of the cryptocurrency it supports. This explains the ‘core’ in its name. It regularly syncs with the network to ensure you have the correct and updated version. That way, you’re running a full node of the protocol.
A node is a computer that stores a complete copy of the blockchain. The more nodes in a particular network and the more spread out they are, the more decentralized the network is. So, by downloading a core wallet, you add a node to the network, making it more decentralized.
Pros and Cons of Using a Core Wallet
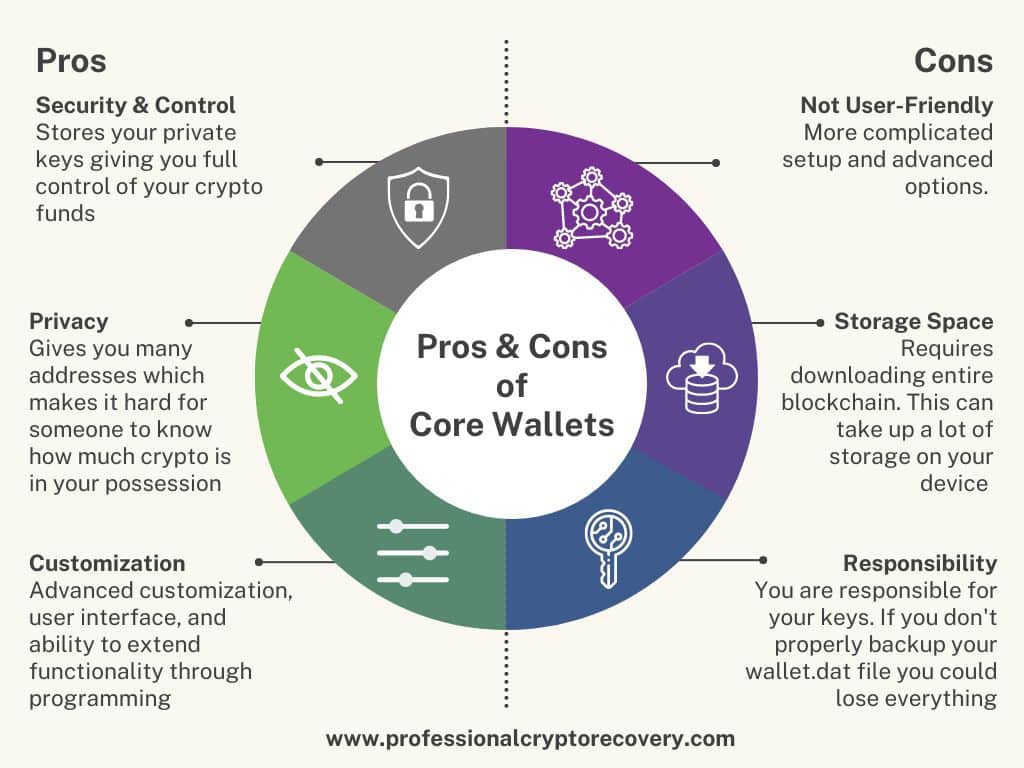
Some big advantages offered by core wallets include:
- Security and Control: A core wallet stores your private keys in your device. This gives you full control of your crypto funds. It also means that your funds are more secure than they would be in a custodial wallet, which is maintained by a third party.
- Privacy: Given the transparent nature of blockchain technology, spying on wallet addresses is quite common. Anyone can see all the transactions involving your wallet by using a blockchain explorer. They can also use this information to calculate your wallet balance. This is something not all crypto users are comfortable with. To solve this problem, core wallets allow the user to generate a new public address for each transaction. So, when you want to receive crypto, you can give out a new address every time. This makes it hard for an on-chain spy to calculate the exact amount of crypto in your possession. Some core wallets, like Bitcoin Core, also let you use Tor as a proxy. Doing so prevents your ISP and hackers from associating your crypto payments with your IP address.
- Customization: A core wallet gives you advanced customization options that allow you to tweak the settings to your liking. The wallet also allows users to modify and extend its functionality through programming. You can change the UI, integrate mobile apps and dApps, and even add a built-in mini-exchange. Of course, doing so requires a good understanding of programming and blockchain technology. If anything goes wrong, you can easily lose all the funds associated with your wallet.
This brings us to the disadvantages of core wallets.
- Not User-Friendly: Setting up a core wallet and using it is a more complex experience than a regular wallet application. It can be difficult and confusing. Furthermore, taking full advantage of all its features requires lots of technical knowledge. For example, customizing the UI, automating transactions, and integrating other applications require advanced programming skills. Generating a new public address for every transaction can also be a bit tedious if you have a high volume of transactions. These make core wallets less user-friendly for non-technical users.
- Storage Space: A core wallet requires you to download the complete blockchain. This means downloading a huge ledger that gets bigger with time. For example, the current size of Bitcoin is around 450 GB. This size increases by about 5 GB a month as more transactions are carried out. Depending on your internet connection, such a big file takes a long time to download and sync with the rest of the blockchain.
- Responsibility: Since core wallets are non-custodial, you’re responsible for your private keys. You have to be extra careful not to lose or forget them. This is because doing so means losing access to the funds stored in the wallet.
Popular Core Wallets
Some popular core wallets include:
- Bitcoin Core: Released in 2009, this is the original core wallet and first ever Bitcoin wallet. Since then, it has been developed and maintained by developers in the Bitcoin community. It is available for Windows, Mac, and Linux and requires around 450 GB of space.
- Litecoin Core: This is the official full-node client for Litecoin. It was built by the same engineer who created Litecoin, Charlie Lee. Compared to Bitcoin Core, this wallet requires less space because its blockchain is smaller. Currently, you need around 25 GB to download the wallet.
- Dogecoin Core: This is the official full-node client for the most popular meme coin, Dogecoin. It contains the entire Dogecoin blockchain and is actively maintained by the Dogecoin community.
- Dash Core: This core wallet contains the entire Dash blockchain. It allows users to send, receive, and manage their Dash balances while running a full node for the blockchain. The wallet requires around 10 GB of space.
Common Problems with Core Wallets
Here are some common issues you may run into when using a core wallet
Lost password/passphrase
Probably the most common problem with a core wallet is losing your password or passphrase. If you’ve been sitting on your bitcoin, it may have been a long time since you’ve decrypted (put in your password/passphrase) your wallet.dat file.
Syncing issues
Core wallets regularly sync. This ensures that each node has the full and correct history of transactions. However, given how big some of these wallets get, syncing requires an excellent internet connection. If you don’t have one it may take weeks or even longer, during which you’ll be unable to send and receive cryptocurrencies.
File issues
Core wallets use a file called wallet.dat to store private keys. If this file is corrupted, lost, or inaccessible for some reason, you’ll have problems accessing the funds associated with your wallet.
There’s also the risk of a stolen wallet.dat file. Hackers can use malware to find and steal the file and the private keys stored inside. This will give them access to the funds in your wallet.
Compatibility issues
Compatibility issues arise when you try to use your wallet with a cryptocurrency it’s not designed for. For instance, if you try to use Litecoins with Bitcoin Core, it will not work.
You might also experience issues due to incompatible scripts during customization. This happens if you use a script that’s incompatible with the core wallet’s built-in scripting language.
Conclusion
There are many core wallets for different cryptocurrencies. These include Bitcoin Core for bitcoin, Litecoin Core for Litecoin, Dogecoin Core for Dogecoin, etc. Overall, they provide an excellent way to store cryptocurrencies.
Due to their technical requirements, they are a popular option among enthusiasts who know how to navigate the worlds of crypto and blockchain. But even with the right knowledge, it’s not uncommon to run into issues with your core wallet.
If it’s something you can’t solve by yourself, we have all the professional help you need to recover your digital assets. Don’t get stuck with a core wallet full of bitcoin you can’t access. At Professional Crypto Recovery, we specialize in helping our clients solve whatever problems they’re experiencing with their core wallets, from unlocking wrong or forgotten passwords to restoring corrupted files. Contact us today to find out how we can help you.
